(a) ΔH < 0; (b) ΔG > 0; (c) ΔS = 0; (d) ΔS > 0; (e) ΔG < 0
- hydrogen bonding in DNA
- van der Waals forces
- charge-charge interactions
- hydrogen bonding in water
- all of the above have equal strength.
| (a) | (b) | (c) | *** (d) *** | (e) |

|

|

|

|

|
(a) alpha helices; (b) beta sheets; (c) 310 helices; (d) random coils; (e) all of the above
| Substrate | Km, µM | kcat, s-1 | Substrate | Km, µM | kcat, s-1 | |
| A | 0.04 | 0.03 | D | 8 | 0.7 | |
| B | 0.2 | 0.0004 | E | 80 | 40000 | |
| C | 2 | 300 | F | 1200 | 2000 |
- A saturated fatty acid at the 1 and 2 positions.
- An unsaturated fatty acid at the 1 and 2 positions.
- A saturated fatty acid at the 1 position and an unsaturated fatty acid at the 2 position.
- An unsaturated fatty acid at the 1 position and a saturated fatty acid at the 2 position.
- at reactions involving carbohydrate substrates.
- at reactions with small negative ΔG values.
- at reactions with large negative ΔG values.
- at reactions for which the products are chiral.
(a) anabolic; (b) catabolic; (c) amphibolic (d) anaplerotic
- may function in heat production, especially in hibernating animals.
- is a defense against bee venoms that act as uncouplers of electron transport and ATP production.
- is a regulatory mechanism for the transport of carbon compounds in and out of the mitochondria.
- is part of the "Q cycle."
- Malonyl ACP is used as a temporary catalytic carrier of two carbon units (acetyl ACP). None of the carbons from malonyl ACP end up in the product fatty acid.
- Malonyl ACP transfers only one carbon to the nascent fatty acid during the condensation step.
- Only even numbers of malonyl groups are used in fatty-acid biosynthesis.
- Malonyl ACP is decarboxylated during the condensation step.
- to increase the production of CTP.
- to decrease the production of CTP.
- There is no reason to believe that GTP should have an effect on the production of CTP.
- This question cannot be answered without also knowing the cellular level of ATP.
(a) DNA replication; (b) transcription; (c) translation;
(d) all of the above; (e) none of the above.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (2 points each):
gly ile val glu gln cys cys thr ser ile cys ser leu tyr gln leu glu asn tyr cys asn
At pH 7.0, what will the net charge on this peptide be?
-2. The only side chains that will be charged at pH 7 are the two glutamate residues, each of which will carry a -1 charge. The amino terminus will be positively charged and the carboxy terminus will be negatively charged. So the total charge is -1 -1 -1 +1 = -2. (Correct answer will receive full credit regardless of how explained; an incorrect answer with some reasonable ideas in it will get up to 1 point.)
Metal ions; cosubstrates; prosthetic groups; water; bound substrates or intermediates; carbohydrate; lipid
(half-point for each of these items up to four of them. Coenzyme is a valid substitute for "cosubstrate" or "prosthetic group".)
(note: The helical CD peak happens to be negative, but that has no bearing on your answer.)
Myoglobin: it is almost entirely helical, whereas immunoglobulins are almost entirely β-sheet proteins.
(2 points of you got myoglobin, with or without explanation)
Membrane-associated proteins
(2 points for membrane-associated, membrane-bound, or integral membrane. Something vaguer like hydrophobic will get 1 point.)
2n-3
(A student who counts all the ketoses for 3 ≤ n ≤ 7 and gets it right (1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 16) = 31 gets 1 point.)
(One point each; proteins instead of membrane proteins is okay.)
_pyruvate_ + HS-CoA + NAD+ → _acetyl CoA_ + CO2 + _NADH_ + H+.
(b) Light in that wavelength range does not penetrate the water readily, so aquatic photosynthetic organisms employ _antenna_ pigment molecules that absorb shorter-wavelength light and pass the energy thus acquired on to chlorophyll via Förster resonances.
(full credit for accessory rather than antenna; half-credit for carrier.)
5'-C-G-T-C-A-C-T-G-C-A-G-G-A-A-G-A-T-G-C-A-3'
3'-G-C-A-G-U-G-A-C-G-U-C-C-U-U-C-U-A-C-G-U-5'
(if you leave off the 3' and 5' designations on the strand, deduct a half-point).
glucose to pyruvate and thence to _lactate_, which can then be converted back to pyruvate in the liver.
(full credit for lactic acid in the second answer; alcohol on the first answer gets a half-point.)
and nucleic acid biosynthesis is _tetrahydrofolate_, whereas the most common methylating agent (donor of methyl groups) is _S-adenosylmethionine_.
(something more specific in the first part is okay as long as the idea that it involves tetrahydrofolate works its way in; adenosylmethionine gets full credit on the second part; S-adenosylhomocysteine gets a half-point in the second part).
THOUGHT QUESTIONS:
Answer twelve of the following sixteen questions. If you answer more than twelve, cross out the answers you don't want graded. Otherwise, the grader will score the first twelve.
| Polymer | monomer | significance |
| Protein | amino acid | Proteins serve as enzymes, carrier molecules, structural entities, and control entities. |
| Nucleic acid | nucleotide | Nucleic acids encode functional information (DNA) and provide machinery for turning that encoding into proteins (RNA) |
| Polysaccharide | sugar | Polysaccharides make up structural elements in cells and act as storage centers for energy-producing molecules. |
| Lipids | fatty acids, glycerol, etc. | Lipids are energy-storage molecules and make up membranes. |
(a) (2 points) If a protein is dissolved in deuterium oxide (D2O), which of the hydrogens in the protein will be replaced by deuterons? Be specific.
Hydrogens on main-chain aminde nitrogens; hydrogens in side-chain OH and NH2 or NH3+ groups (ser, thr, asn, gln, tyr, his, trp, lys, arg); hydrogens on N-terminal amine group. Of these, the ones that can readily exchange are those that are fully exposed to solvent; a tyr -OH hydrogen buried deep in a hydrophobic pocket will not exchange rapidly.
(The student need not specify all the amino acids with side-chain OH or NH's; a few examples must be there to show that he or she understands. The point about solvent accessibility need not be stated, but if it is, it can make up for a shortcoming elsewhere in this half of the question).
(b) (2 points) If a long polymer of DNA is dissolved in D2O, which of the hydrogens in the deoxyribose-phosphate backbone will be replaced by deuterons (assuming that the deoxyribose rings remain closed)?
Only hydrogens on the phosphate OH groups, if there are any. The 2'-OH hydrogens on RNA would exchange, but those are absent in DNA. The other hydrogens are either attached to carbons or have been replaced with bonds between O and P or O and C.
(2 points if the student said only phosphate OH hydrogens, even without an explanation. The answer none is almost correct; award 1.5 points.)
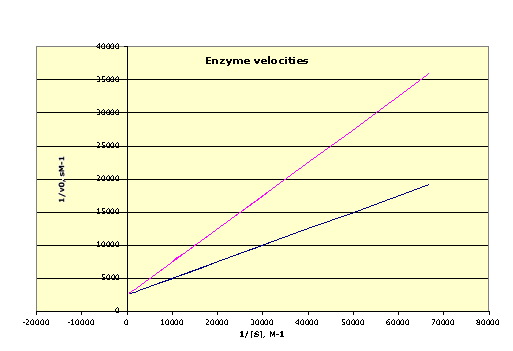
(a) (2 points) The flatter of these two curves represents the kinetics for an uninhibited enzyme. Estimate Vmax and Km for this flatter curve.
Vmax = 4 * 10-4 M s-1 by reading off the Y intercept of the plot as 2500 sM-1 and taking the reciprocal of that.
Km = 10-4 M, taken by following the flatter curve out to its X-intercept as -10000 M-1 and taking the reciprocal of that.
(One point for correct Vmax value and one for the correct Km value. Ordinarily I would require that the units be correct, but since the explanation at the beginning of the problem actually has a unit error in it, you can ignore units this time.)
(b) (2 points) The steeper curve represents the kinetics for the inhibited enzyme. Is the inhibitor that produced this result competitive, noncompetitive, or uncompetitive? Why?
It is competitive inhibition, for which the maximum velocity (which occurs when the substrate is saturating the system) is independent of the presence of the inhibitor.
(One point for getting the mode of inhibition right; one for a plausible explanation. A purely phenomenological explanation, e.g. Vmax is the same, only earns half a point on the explanation.)
Cells maintain control over concentrations of reactants and products so that the ΔG values for all the reactions are slightly negative even thought the ΔGo' values are not.
(2 points for any mention of the distinction between ΔG and ΔGo'; 2 points for the notion that concentration control makes that possible. If the equation relating ΔG to ΔGo' is given, give an extra point if it's needed to bring the total up to 4.)
 |
pyridoxal phosphate |
(Count off a half-point for misspellings.)
(b) (2 points) Describe the role it plays in transamination reactions.
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) serves as the intermediate amine-group acceptor in transamination reactions; the amine is transferred from the nitrogenous reactant to PLP and thence onto the other reactant, which then becomes aminated and the PLP reverts to its starting state.
(Be reasonably generous: the fact that it's the amine acceptor is the most important point.)
(c) (1 point) Are the transamination reactions in which this compound participates sequential / ordered, sequential / random, or ping-pong?
Ping-pong. The covalent attachment of the amine to the PLP molecule must be complete before the amine can be transferred to the other reactant.
(Ping-pong is adequate).
,

is characteristic of transamination.
(a) (3 points) Is this an oxidation-reduction reaction or a simple transfer of a leaving group?
Oxidation-reduction
(b) (1 point) What is the product if R = CH3?
alanine
(Give a half-point for something like methylglycine.)

(You needn't number the carbons and nitrogens.)
 |
Guanine |
 |
chorismate. |
| This molecule is derived from shikimate and can be converted into intermediates that lead in two steps to either phenylalanine or tyrosine; a somewhat longer pathway leads to tryptophan. | |
| (Two points for chorismate or chorismic acid; two points for the fact that it leads to phe, tyr, and trp.) |
 |
This cyclic intermediate is created in a hydroxyl attack on the 2'-OH
group of 3'-phosphoribose or a 3'-phosphoribonucleotide, either on its
own or as part of an RNA polymer.
The cyclic intermediate then decomposes either into
a 2'-nucleoside monophosphate or a 3'-nucleoside monophosphate, with
concomitant breakage of the sugar-phosphate backbone at the 3' position.
The result is that the RNA backbone is broken. These reactions don't occur
in DNA because DNA doesn't have a hydroxyl at 2' to participate in
this reaction. (Drawing: 2 points if it's correct; up to 1.5 points for a partially correct drawing.) (Explanation: 4 points for a plausible explanation. The explanation should include the fact that this intermediate can form in an RNA polymer or a big piece of RNA, and that chain cleavage at the 3' position will occur after the cyclic intermediate breaks up.) |
By the central dogma, [A] = [T], so 0.25 of the bases are T. Therefore the number of bases that are not A or T is 1 -0.25 - 0.25 = 0.5, so fraction(C) + fraction(G) = 0.5. But fraction(C) = fraction(G), so fraction(C) = fraction(G) = 0.25. Probability of a C at any position = 0.25 Probability of a G at any position = 0.25. Probability of CCGG as a group of four consecutive bases = (0.25)4. Thus on one strand the number of instances of this sequence should be equal to the total number of four-base groups, multiplied by (0.25)4. The number of four-base groups is just the length of the strand minus three, so that's essentially 10^6. Thus the number of instances of CCGG on the strand is 10^6 * (0.25)^4 = 10^6 * 0.00390625 >= 3906.25 or roughly 3906 instances. We might think that we would find another 3906 instances on the other strand, but we don't, because CCGG is palindromic. Therefore wherever we find a 5'-CCGG-3' on one strand, we find a 3'-GGCC-5' on the other strand at the same time. So there really are 3906 HpaII sites.
(4 points for the right answer to within 1% if the logic is even close to correct. If the logic is correct (including understanding about palindromic sequences) but the numerical answer is wrong, then award up to three points.)
Types of ribonucleic acid
| Type | Steady-state level |
Size | Role in translation |
| rRNA | 83% | Large | Catalysis and scaffolding in ribosome |
| tRNA | 14% | ~65-90 bases | Carry activated amino acids to translational machine |
| mRNA | 3% | 100-10000 bases | Contains transcribed template to be used in translation |
| sRNA | < 1% | 50-1000 bases | varies |
See fig. 21.13 in Horton. Each student should describe at least three of the four.
- An activator with a ligand bound to it will bind to the promoter site and stimulate transcription, whereas if it has no ligand bound to it, it won't bind.
- A different kind of activator without ligand bound will bind to the promoter and stimulate transcription, but only if ligand is absent; if ligand is present, the activator will not bind and stimulate.
- A repressor without ligand bound can bind at the promoter site and inhibit transcription. If ligand binds to the repressor, the repressor is inactivated, i.e. it falls away from the promoter site so that transcription can begin.
- A different repressor with ligand bound will bind to the promoter site and interfere with transcription. If the repressor does not have ligand bound, it will not interfere with transcription. The ligand in this case is called a corepressor.
An Okazaki fragment is a piece of duplex DNA, typically less than 1000 bp in length, produced along the lagging strand during DNA Polymerase III replication. It will have an RNA primer at its 5' end. An Okazaki fragment appears as 5'-3' DNA replication proceeds on the lagging strand, locally working in the opposite direction from the direction in which the DNA Polymerase III machine is moving. Each fragment must be ligated with its neighbors upstream and downstream along the lagging strand. The ligation requires that we remove the RNA primer and at the 5' end, and then splice the 5' end of the Okazaki fragment with the 3' end of its upstream neighbor. This removal of the RNA primer and the ligation require DNA polymerase I and DNA ligase.
(2 points for a decent definition that includes the mention of the RNA primer. 2 points for the explanation of where they come from and how they get cleaned up and spliced together.)
The spliceosome is the site at which the original mRNA created from a gene is shortened by removal of introns from the raw mRNA, leaving behind a spliced mRNA molecule consisting of the exons left behind after removal of the introns. This splicing process requires that there be recognition sequences near the 5' and 3' ends of each intron so that the spliceosomal machinery can know where to break the mRNA chain and then sew it back together. The process involves a set of enzymatic reactions that employ both protein and sRNA molecules as catalysts.
(1 point for articulating what happens; 1 point for mentioning exons and introns; 1 point for how the spliceosome knows where to cut and sew.)
(b) (1 point) What kinds of organisms have spliceosomes?
Eukaryotes. Prokaryotes do not have introns; each mRNA molecule is translated directly into protein, often starting as the mRNA is created through transcription.
(Eukaryotes is sufficient for full credit. Half point for something pertinent like higher organisms).
Pyrophosphate will hydrolyze nonenzymatically to two molecules of phosphate:
PPi → 2 Pi
This reaction has a substantially negative ΔG associated with it. It is effectively irreversible, thereby rendering the parent reaction
ATP → AMP + PPi
effectively irreversible as well, since the product of the parent reaction doesn't stay around long enough for reversal to occur.
(The hydrolysis of pyrophosphate is worth 2 points; some discussion of what's happening to ATP (or other nucleotides) will provide the other two points.)
The template strand is poly(dC), so the mRNA created will be complementary to that--i.e., it will be poly(G). Therefore no matter what reading frame we start in, the codons recognized during protein synthesis will be GGG, which will code for glycine. So we should get, under ideal conditions, N glycines in a row in the protein product produced at the ribosome.
(2 points for recognizing that the mRNA will be poly(G); 2 for using the table correctly and seeing that we will be getting polyglycine.)